Molecular and Tumor Pathology
Overview
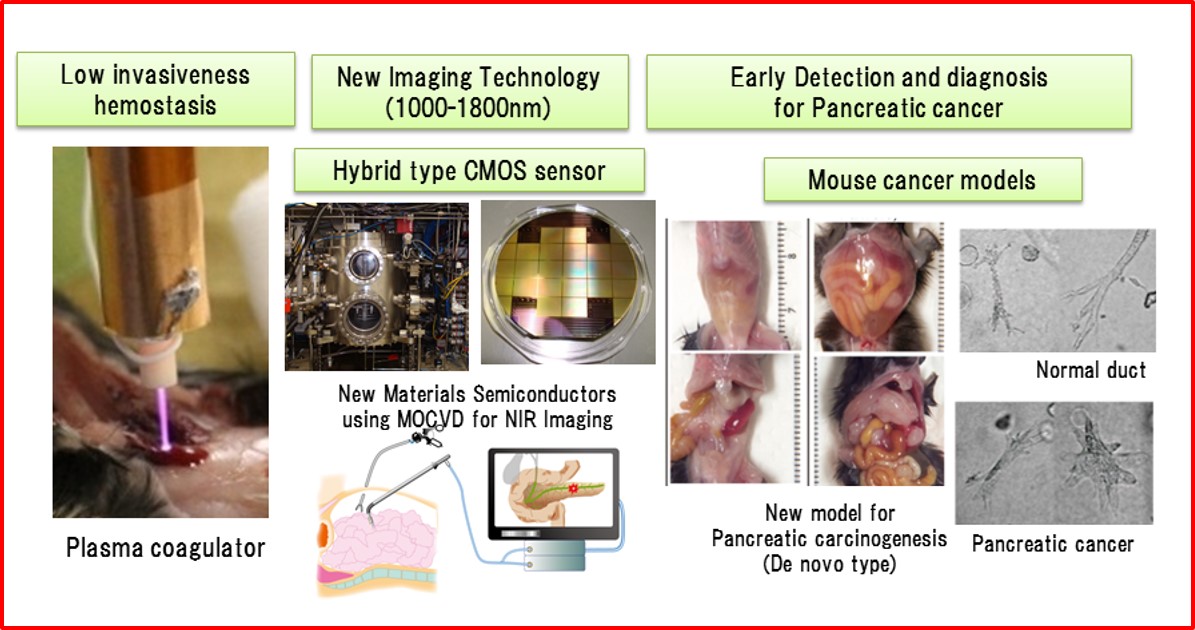
Our research goals are to produce scientific evidence of medical care and promote the progression and development of high-quality medical services. Therefore, we have tackled the reproduction of human cancer and inflammation in mice by applying genetically engineered technology and investigating the onset and progression of the disease using histopathological and molecular biology techniques. On the other hand, we have been trying to introduce the microfabrication and semiconductor manufacturing process used in the electronics industry into technologies in pathology. Indeed, we have succeeded in the evolved the hemostatic equipment using plasma technology that has been used for semiconductor processing. Moreover, near-infrared cameras made from InGaAs semiconductors help to reliably detect small lymph nodes of 5 mm or less in adipose tissue. Furthermore, by using these technologies for pathological analysis, we expect to achieve new discoveries that lead to an understanding of diseases.
[ We conduct research collaborating with clinical departments by understanding diseases and creating medical devices, returning the knowledge of pathology to society.]
Professor:
Yuzuru Ikehara, M.D., Ph.D.
TEL: +81-43-226-2057
FAX: +81-43-226-2058
e-mail: yuzuru-ikehara●chiba-u.jp
URL: https://www.m.chiba-u.jp/class/pathol1/index.html
※ Please change "●" mark to at-mark if you send emails.

Research & Education
Pathology & Oncology
We analyze pathology to understand mechanisms of etiology and progression of disease (especially cancer) in humans. Generation of genetically-engineered mouse models that recapitulate human cancers, and immortalized cell culture from specific cells culture are basic approaches to study.
Glycobiology
We have developed new biomarkers evaluating disease progression such as liver fibrosis using glycol-proteomic approaches.
Near-Infrared Light Imaging
Based on our success to create a camera visualizing pathophysiology detected in1000-1800nm near infrared wave length, we try to establish new diagnostic concepts using the imaging technology
Recent Publications
- Ogata H, Akita S, Ikehara S, Azuma K, Yamaguchi T, Maimaiti M, Maezawa Y, Kubota Y, Yokote K, Mitsukawa N, Ikehara Y. Calcification in Werner syndrome associated with lymphatic vessels aging. AGING (Albany NY) 13(24):25717-25728, 2021.
- Sakakita H, Yamada H, Shimizu T, Fujiwara M, Kato S, Kim J, Ikehara S, Shimizu N, and Ikehara Y.Effects of electric charges on serum protein aggregation induced by a low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma. J Phys. D: Appl. Phys.2021 Vol 54(21) 215201.
- Yokoyama N, Sivakumar T, Ikehara S, Akimoto Y, Yamaguchi T, Wakai K, Ishikawa K, Hori M, Shimizu, T, Sakakita H, Ikehara Y. Growth inhibition effect on Trypanosoma brucei gambiense by the oxidative stress supplied from low-temperature plasma at atmospheric pressure Selected Topics in Applied Physics (STAP) Articel, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2021. 60(2) 020601
- Pecori F, Akimoto Y, Hanamatsu H, Furukawa J, Shinohara Y, Ikehara Y, Nishihara S. Mucin-type O-glycosylation controls pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells via Wnt receptor endocytosis. J. of Cell Sci. 133: jcs245845 2020
- Akita S, Yamaji Y, Takeuchi N, Wakai K, Azuma K, Nakagawa A, Fujimoto H, Sangai T, Nagashima T, Mitsukawa N, Ikehara Y. Detection of Nonpalpable Tiny Axillary Lymph Nodes Surrounded by Adipose Tissue Using a Near-Infrared Camera. Lymphat Res Biol. 2020 Feb 12. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2019.0022.
- Yamaguchi T, Ikehara S, Akimoto Y, Nakanishi H, Kume M, Yamamoto K, Ohara O, Ikehara Y TGF-β signaling promotes tube-structure-forming growth in pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 2;9(1):11247.
